We were the first to introduce Synthetic Fibres in India way back in the 50s
Fibre is considered the raw material in the textile industry, used to spin into yarn or processed into various textiles such as woven fabric, knitted fabric, lace, felt, and non-woven materials through appropriate interlacing methods. This process is crucial for fabric companies in India that rely on high-quality fibres to produce diverse textile products for both domestic and international markets. By optimizing the use of fibres, these companies play a significant role in the global textile supply chain.
Fibre are broadly classified into 2 categories –
- Natural Fibre
- Man Made
Natural fibre, any hairlike raw material directly obtainable from an animal, vegetable, or mineral source and convertible into non-woven fabrics such as felt or paper or, after spinning into yarns, into woven cloth. A natural fibre may be further defined as an agglomeration of cells in which the diameter is negligible in comparison with the length.
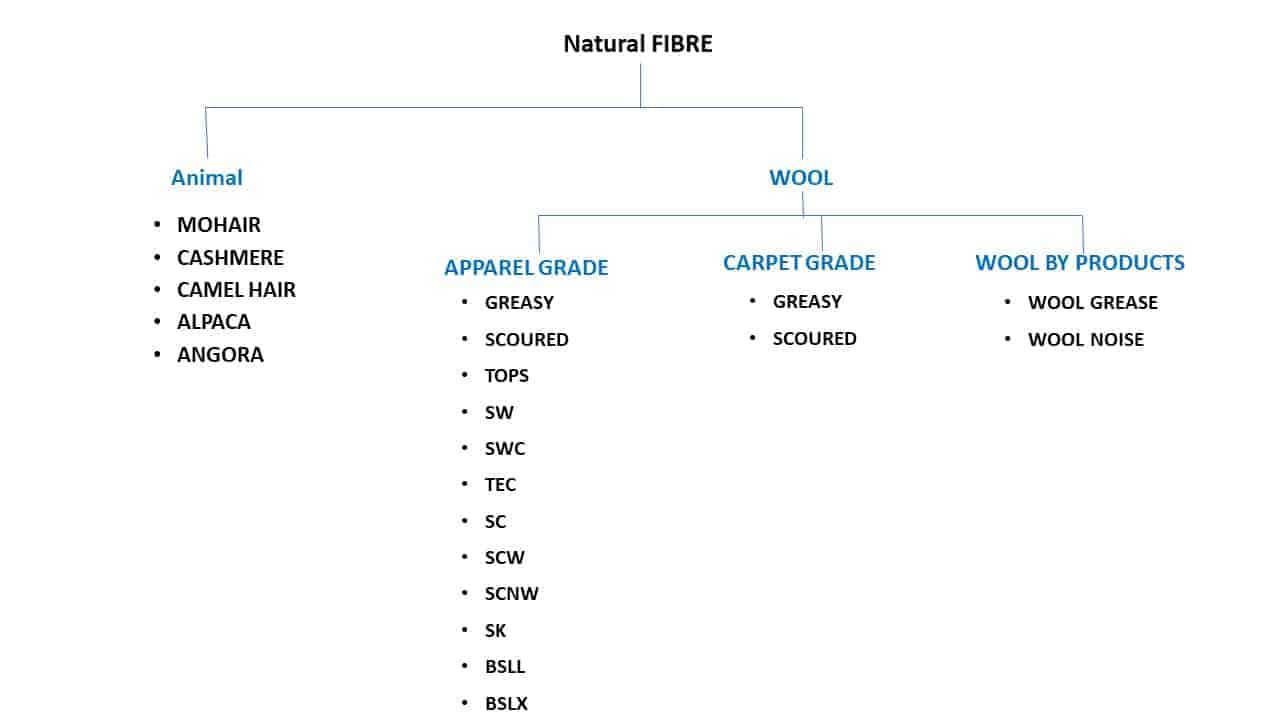
Natural Fibre are further divided into 2 type
- Animal Hair
- Wool
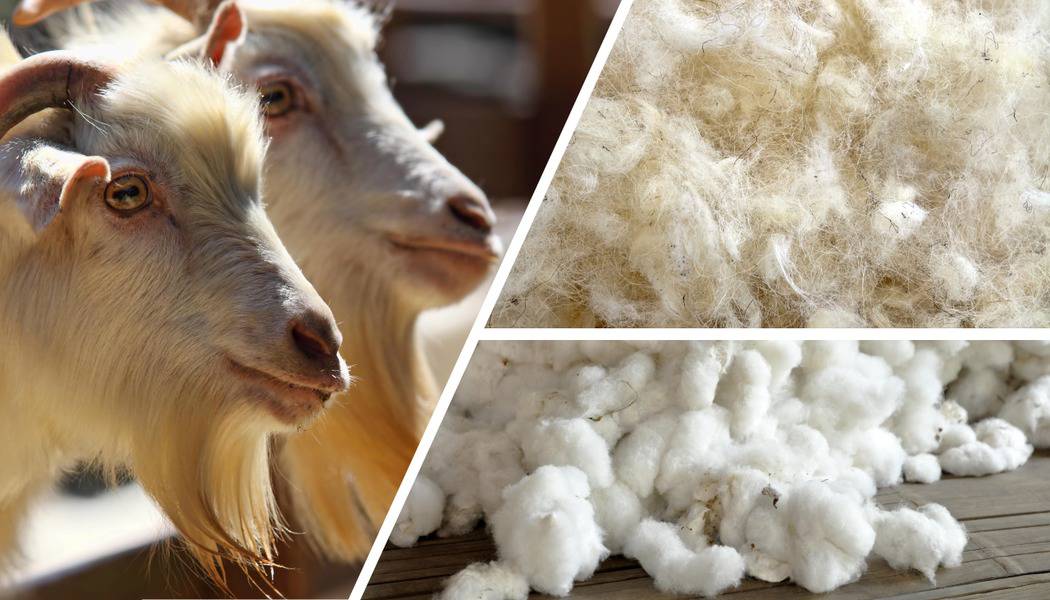

Type of Animal Hairs Fibre
- Mohair
- Cashmere
- Camel Hair
- Alpaca
- Angora
Wool Fibre are divided into 3 category
- Apparel Grade
- Carpet Grade
- Wool by Product
Man Made fibre, a type of fibre that is made artificially, such as polyester, nylon or rayon, rather than occurring naturally, like cotton or wool. Man mande fibre are fibre whose composition, structure and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process.
Man-made fibres are spun and woven into a huge number of consumer and industrial products, including garments such as shirts, scarves, and hosiery; home furnishing such as upholstery, carpets etc.
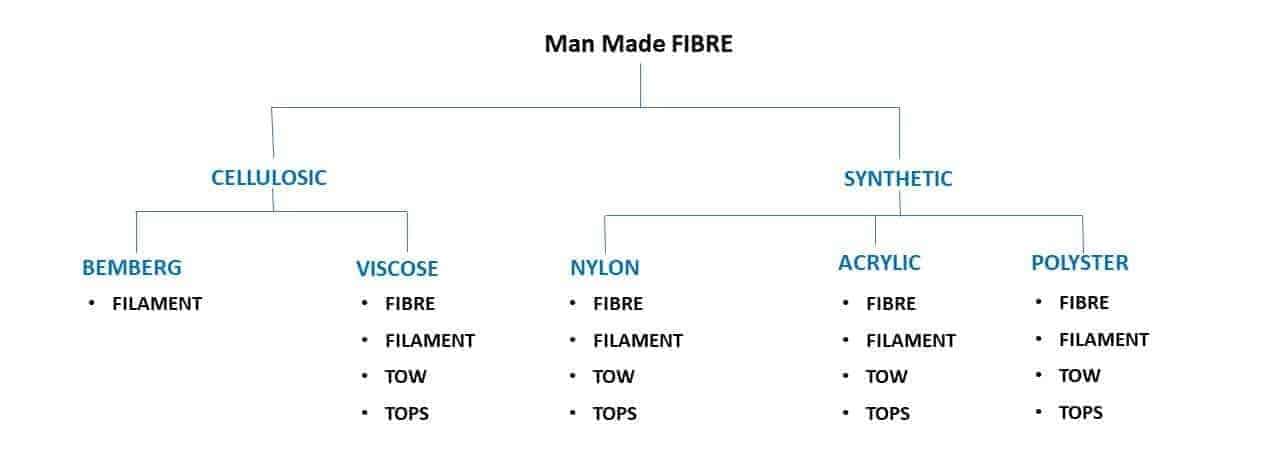
Man Made Fibre are further divided into 2 category –
- Cellulosic
- Synthetic
Damodar Menon International is a global trading partner specializing in the buying and supplying of natural fibres like cotton and wool, as well as synthetic fibres. Their expertise in sourcing high-quality raw materials is vital for fabric companies in India, which depend on these fibres to produce a wide range of textiles, including woven and knitted fabrics.
